PyTorch 60min教程
PyTorch 60min教程
什么是PyTorch
基于Python的科学计算包,有以下目标:1.替代NumPy以支持GPU;2.支持深度学习领域,以提供灵活性和速度
开始
Tensors
Tensors与Numpy的ndarray (n维数组)很像,并且多了在GPU上运算的能力。
import torch
构建一个5x3的矩阵,很多方法:
x = torch.empty(5, 3)
x = torch.zeros(5, 3) # 推荐。
x = torch.rand(5, 3)
print(x)
直接从数据构建tensor
x = torch.tensor([5.5, 3]); print(x)
# tensor([5.5000, 3.0000])
获得大小
print(x.size())
Tensor的操作
In [19]: x = torch.rand(5,3)
In [20]: y = torch.rand(5,3)
In [21]: x+y
Out[21]:
tensor([[0.5382, 1.8239, 0.2713],
[1.0294, 1.0171, 1.0428],
[1.4945, 1.1763, 1.2707],
[1.8769, 0.7077, 1.7810],
[1.7013, 1.4604, 0.4329]])
与numpy转换
tensor 转ndarray
a = torch.ones(5)
print(a)
tensor([1., 1., 1., 1., 1.])
b = a.numpy(); print(b)
ndarray转tensor
In [28]: import numpy as np
In [29]: a = np.ones(5)
In [30]: b = torch.from_numpy(a)
cuda tensors
x
tensor([[0.3044, 0.9737, 0.1535],
[0.8429, 0.8485, 0.0721],
[0.7615, 0.7300, 0.5238],
[0.9435, 0.3953, 0.9996],
[0.7440, 0.8475, 0.0657]])
直接在GPU上创建tensor
y = torch.ones_like(x, device='cuda')
y
tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]], device='cuda:0')
CPU上的tensor 转到GPU上
x = x.to(device)
GPU转到CPU
z = x+y
z.to('cpu', torch.double)
自动微分
Pytorch所有神经网络的核心是autograd包。
torch.Tensor是该包的核心类。如果设置了它的属性.requires_grad为True,它将追踪其上所有的操作。当完成计算之后,调用.backward()即可自动计算素有的梯度。该tensor的梯度存在.grad属性中。
要想阻止张量追踪,可以调用.detach()
Tensor 和 Function相互连接构成非循环图 (想象一下一个tensor,然后用function计算...)。每个tensor有一个.grad_fn属性用来记录创建他们的Function,除了用户自己创建的tensor。
如果想要计算导数,可以在Tensor上调用`.backward()。
In [68]: import torch
In [69]: x = torch.ones(2,2,requires_grad=True)
In [70]: x
Out[70]:
tensor([[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]], requires_grad=True)
In [71]: y = x + 2
In [72]: y
Out[72]:
tensor([[3., 3.],
[3., 3.]], grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
In [73]: y.grad_fn # 因为y是计算产生的,所以有grad_fn
Out[73]: <AddBackward0 at 0x7fa2dc92a198>
设置
requires_grad的值,以便tensor能够追踪创建它的函数。
In [81]: a
Out[81]:
tensor([[ -1.2560, -11.1015],
[ -2.4457, 1.9479]])
In [82]: print(a.requires_grad)
False
In [83]: a.requires_grad_(True)
Out[83]:
tensor([[ -1.2560, -11.1015],
[ -2.4457, 1.9479]], requires_grad=True)
a.requires_grad=False
a.requires_grad=True
然后可以调用
.backward进行求导
out.backward()
print(x.grad) # 即求`d(out)/dx`
神经网络
可以使用torch.nn来构建神经网络。
nn依赖于autograd(自动梯度)来定义模型。nn.Module包含layers,和一个forward(input)方法,并返回output
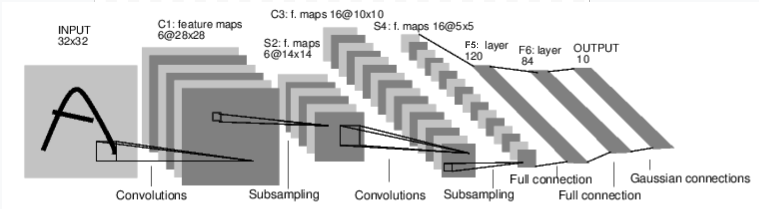
一个典型的神经网络训练:
- 定义神经网络,使它有一些可学习的参数(或权重)
- 迭代输入数据集
- 通过神经网络处理输入
- 计算loss (与正确的输入有多远)
- 将梯度传播到神经网络的参数
- 更新神经网络,通常用很简单的更新规则:
weight = weight - learning_rate * graient